Home
Learning
Multimedia
Other
Contact
Learning Theories
Learning theories come from psychological theories based on empirical research and attempt to explain how people learn. Although many theories were drawn from work with children, they may be applied to other groups of learners. Double-click the image below to go to YouTube for a jazz overview before reading the descriptions provided.
(uploaded by pvbsTeach)
Behaviorism
Behaviorists define learning as an external, observable change in behavior. In the early research learning is often viewed as a response to stimuli and the brain is seen as a “black box” with no explanation of what happens in the brain during the learning process. Key behaviorists include:
- Pavlov (early 1900’s, translated into English in 1927)
- Watson (1914)
- Skinner (1938)
Behaviorist instruction is primarily didactic in nature and is generally passive as the learner is considered an empty vessel and the instructor “fills” the learner with knowledge. A lectureis an example of a behaviorist approach.
Cognitivism
Cognitivism (cognitive psychology) has been a predominant perspective within learning research. Cognitivism explores the mental process that occur when learning takes place. There are a variety of cognitive theories of learning. Many of them address how learning occurs in the brain and process of memory (short and long term) and how information is processed.
Constructivism
Learning is an active process where learners construct new ideas or concepts based upon their current and/or past knowledge. In constructing knowledge, the learner:
- selects and transforms information
- constructs hypotheses
- makes decisions using a cognitive structure
Social Learning Theories
Theories that describe how society and social interactions impact learning are social learning theories. Bandura’s theory is one of the most well-known and was based in part upon Vygotsky’s work.
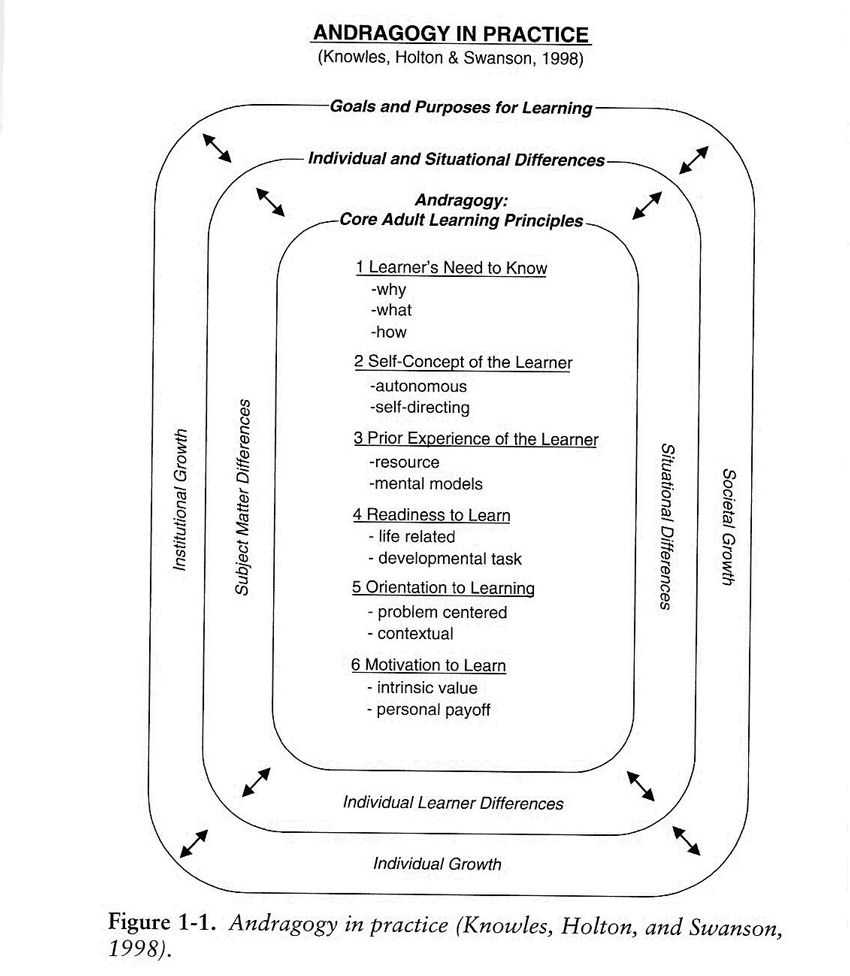
Andragogy, Adult Learning Principles
Adults learn differently from how children learn, and for a long time no one paid attention to this fact, until Malcolm Knowles came along and wrote about the adult learner being a neglected species. Knowles, who earned the title "father of adult learning," purported that there are six core principles which characterize adult learners and differentiate them from children. Andragogy is the theory that explains adult learning principles.
Some Tips About Training Adult Learners
Adult learners are goal-oriented. It’s always good practice to talk with them about how what they are learning applies to their academic and/or work situations and the goals they’ve set for themselves.
Respect your learners’ prior knowledge and experiences. Provide ample opportunities for them to share with each other.
Help learners find the learning environments that work for them so there’s less fear and insecurity.
Encourage learners to immediately begin using newly acquired skills.
Provide opportunities for them to learn in a variety of ways—through a blended format of delivery—which uses a combination of technology (elearning, CBL, CDs, Internet, Social Media, etc.) and interactive classroom contact time. Cater to all modalities: visual, auditory and kinesthetic learners.
© 2012 Judith Roberts. All rights reserved.